Talk about the different traversals you’ve done in your code; illustrate with a diagram, if you have to.
There are three traversals I’ve done in my code. They are pre-order, in-order, and post-order. The three are kinds of depth-first traversals. They traverse the binary tree recursively. We’ll be using this binary tree below as an example for illustration.
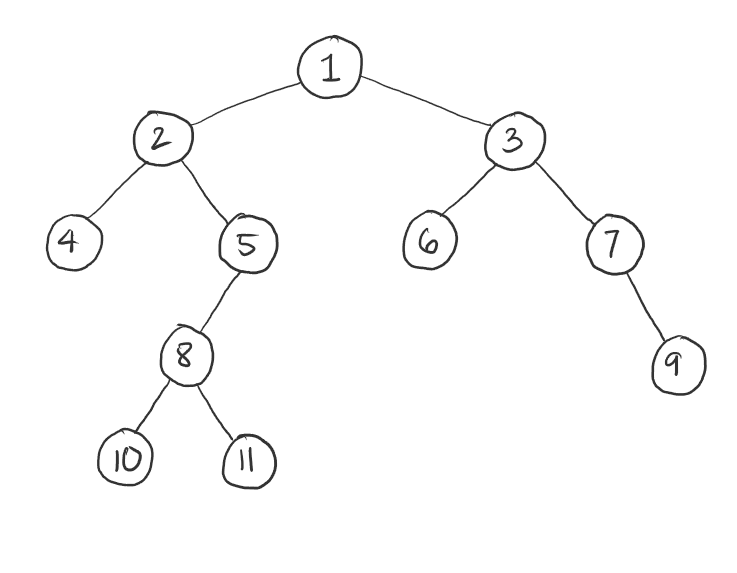
Pre-order traversal would visit the root first, then the left side of the tree and lastly the right. (Root –> Left –> Right)

In-order traversal is somewhat the correct order wherein we would visit first the left side of the tree, then the root, and lastly the right. (Left –> Root –> Right)

Post-order traversal would visit first the left side of the tree, then the right, and lastly the root. (Left –> Right –> Root)

What is the time complexity of a traversal?
The time complexity of a traversal in a binary tree is always O(n). This is for both worst case and average case. This is because you would have to traverse, or say visit all of the nodes in the tree, like a linked list. However, when we say space complexity of a binary tree, it would be O(log n).
Code Used:
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.parent = None
self.left = None
self.right = None
# stack implementation
class Stack:
def __init__(self):
self.items = []
def push(self, item):
self.items.append(item)
def pop(self):
if (self.size() == 0):
raise "Nothing to remove since stack is empty!"
else:
return self.items.pop()
def display(self):
print(self.items)
return
def size(self):
return len(self.items)
# binary expression tree implementation
class BinaryExpressionTree:
def __init__(self):
self.stack = Stack()
def preorder(self, root):
if root:
print(root.data, end = " "),
self.preorder(root.left)
self.preorder(root.right)
return
def inorder(self, root):
if root:
if root.data in "0123456789":
print(root.data, end = "")
else:
print("(", end = "")
self.inorder(root.left)
print("", root.data, "", end = "")
self.inorder(root.right)
print(")", end = "")
return
def postorder(self, root):
if root:
self.postorder(root.left)
self.postorder(root.right)
print(root.data,end = " ")
return
def evaluate(self, root):
# empty tree
if root is None:
return 0
# leaf node
if root.left is None and root.right is None:
return int(root.data)
# evaluate left tree
left_sum = self.evaluate(root.left)
# evaluate right tree
right_sum = self.evaluate(root.right)
# check which operation to apply
if root.data == '+':
return int(left_sum + right_sum)
elif root.data == '-':
return int(left_sum - right_sum)
elif root.data == '*':
return int(left_sum * right_sum)
else:
return int(left_sum / right_sum)
input_dat = []
# reading input.dat
with open('Week 7\input.dat', 'r') as input:
input.readline()
input.readline()
for line in input:
input.readline()
input_dat.append(line.split())
# print(input_dat)
# evaluating the expression tree from the output
expressionTrees = []
for expression in input_dat:
expressionTree = BinaryExpressionTree()
for character in expression:
if character == "+":
node = Node(character)
node.parent = character
node.right = expressionTree.stack.pop()
node.left = expressionTree.stack.pop()
expressionTree.stack.push(node)
continue
elif character == "-":
node = Node(character)
node.parent = character
node.right = expressionTree.stack.pop()
node.left = expressionTree.stack.pop()
expressionTree.stack.push(node)
continue
elif character == "*":
node = Node(character)
node.parent = character
node.right = expressionTree.stack.pop()
node.left = expressionTree.stack.pop()
expressionTree.stack.push(node)
continue
elif character == "/":
node = Node(character)
node.parent = character
node.right = expressionTree.stack.pop()
node.left = expressionTree.stack.pop()
expressionTree.stack.push(node)
continue
else:
expressionTree.stack.push(Node(character))
expressionTrees.append(expressionTree)
# print(stackForExpressionTree)
# print()
# printing the outputs
for i in expressionTrees:
i.preorder(i.stack.items[0])
print()
i.inorder(i.stack.items[0])
print()
i.postorder(i.stack.items[0])
print()
print(i.evaluate(i.stack.items[0]))
Sample Input
3
5
5 3 2 + *
7
9 1 4 5 * + -
9
2 2 / 5 1 8 + * *Sample Output
* 5 + 3 2
(5 * (3 + 2))
5 3 2 + *
25
- 9 + 1 * 4 5
(9 - (1 + (4 * 5)))
9 1 4 5 * + -
-12
* / 2 2 * 5 + 1 8
((2 / 2) * (5 * (1 + 8)))
2 2 / 5 1 8 + * *
45